Currently, most websites work on the Apache web server, which is often used by hosting companies due to its capabilities and the lack of license fees. An alternative and increasingly used choice is Litespeed.
What is Litespeed?
Litespeed is a commercial web server known primarily for its excellent performance compared to other available solutions such as Apache. It is worth mentioning that despite an improvement in performance, it has full compatibility with Apache, so you can use the mod_rewrite function and the capabilities of the .htaccess file.
Litespeed and Apache performance test
To show the differences in performance between Litespeed and Apache, we decided to perform tests. The checking platform was the popular WordPress, for which the official Litespeed plugin LSCache is available. To maintain the test’s credibility, two identical applications were installed – one on Apache and the other on Litespeed. Two methods of page caching were also used: Memcached and Redis.
The following tests were performed on the latest version of WordPress (5.4). The same additional plugins and themes were used in each test, the only difference was the way the data was cached as described in the attached screenshots. Both Memcached and Redis support was implemented by using the LSCache plugin.
Litespeed server performance tests with LScache and Redis
We did several tests on a WordPress-based website – it is a blog with a dozen entries – it is a real website – a tourist blog. The test page was not specially prepared – it is a site that has been working on our servers for over a year and is a regularly updated tourist blog.
The test results are presented below:
Litespeed: WordPress without cache

Litespeed: WordPress + Memcached

After tests, it can be clearly stated that using the cache is necessary for the website to work quickly. There is also a noticeable reduction in TTFB after using the cache on the page.
The differences in TTFB (time to first byte) for Litespeed with different cache options enabled are shown in the table below:
| TTFB (the lower the better) | The time difference | |
| WordPress without cache | 258 ms | +145 ms |
| WordPress + Memcached | 165 ms | +93 ms |
| WordPress + Redis | 113 ms | 0 ms |
If you are using the Litespeed server, it’s worth enabling the LScache plugin – it is a dedicated WordPress plugin provided by the developers of the commercial version of the Litespeed server. As you can see during the test, it was shown that using just such a caching method compared to the non-cache version can reduce server requests by up to half.
Apache server performance tests with cache and memcached
How did the test on the popular Apache server? We performed identical tests for the same application (travel blog on WordPress) using Apache instead of Litespeed. The test results are presented below:
Apache: WordPress without cache

Apache: WordPress + Memcached
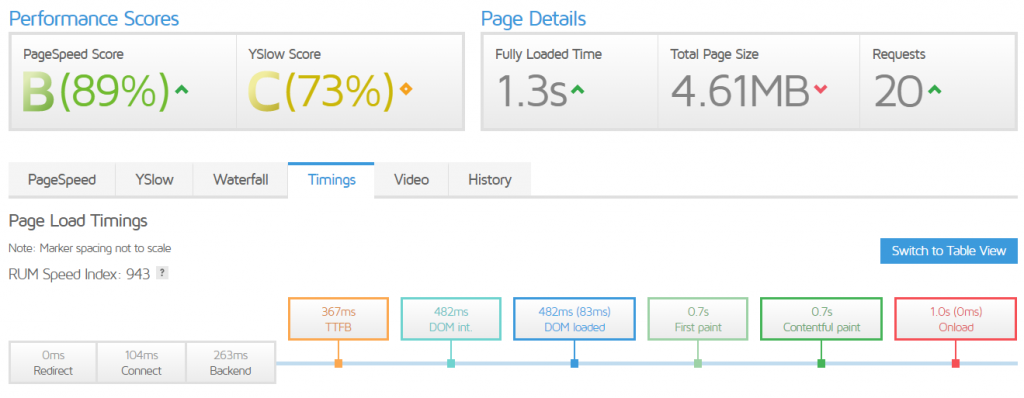
Due to the possibility of using Redis only on premium-ls servers (Litespeed server) no tests were performed for the Apache + Redis configuration.
Also on Apache, cache usage shortened TTFB and the total page load time.
| TTFB (the lower the better) | The time difference | |
| WordPress without cache | 378 ms | +11 ms |
| WordPress + Memcached | 367 ms | 0 ms |
Summary of Litespeed vs Apache performance tests
After testing, it is clearly seen that for both web servers (Apache or Litespeed) the use of cache significantly reduces page loading time.
In the chart below, the lower, the better.

After using a Litespeed server, the page load speed can be significantly reduced compared to an Apache server. The use of the Redis-based cache system has reduced the page loading by half.
We have collected the differences in page load time (whole page load time) and TTFB (time to first byte) in the table below:
| Loading time ( the lower the better) | Time difference | TTFB (the lower the better) | TTFB difference | |
| Litespeed: WordPress without cache | 1.4 s | +0.7 s | 258 ms | +145 ms |
| Litespeed: WordPress + Memcached | 1.0 s | +0.3 s | 165 ms | +52 ms |
| Litespeed: WordPress + Redis | 0.7 s | 0 s | 113 ms | 0 ms |
| Apache: WordPress without cache | 1.6 s | +0.9 s | 378 ms | +265 ms |
| Apache: WordPress + Memcached | 1.3 s | +0.6 s | 367 ms | +254 ms |
In the comparison table, you can clearly see that the server (Litespeed, Redis, NVMe) is important for the speed of the website, but also the proper cache configuration on the website. In some cases, you can reduce the page loading time by half.
Own Litespeed + Redis tests at Smarthost.eu
If you want to see for yourself how much your website can speed up – we encourage you to test LiteSpeed packages. Each package based on the commercial LiteSpeed system with LScache and with a dedicated cache system based on Redis can be tested for free for 14 days.
It’s worth having a fast hosting server based on Litespeed and Redis:
| NVMe Storage | Free SSL certificate | Annual Price | |
| nvme-litespeed-mini Order hosting 14 day free trial | 5 GB | Yes | 29 € |
| nvme-litespeed-www Order hosting 14 day free trial | 10 GB | Yes | 59 € |
| nvme-litespeed-store Order hosting 14 day free trial | 20 GB | Yes | 89 € |
| nvme-litespeed-business Order hosting 14 day free trial | 50 GB | Yes | 129 € |
| nvme-litespeed-max Order hosting 14 day free trial | 100 GB | Yes | 199 € |
- A direct connection between Smarthost and Cloudflare - October 2, 2024
- Why is Redis better than Memcached? - September 16, 2024
- What is DMARC and why should you have it? - July 12, 2023